When determining what is the best house insulation, carrying out an examination of where you are most likely to lose heat, and knowing the types of insulation and R values is important. This will reveal where you need better insulation, then you can decide what is best house insulation to suit your particular applications.
This will be based on the highest R-value insulation, within your budget as generally the higher the R-value, the more costly the insulation, paying that little bit extra for the best house insulation will be cheaper in the long run.
R Values to Determine the Best Insulation for a House
To find out what is the best insulation for a house involves understanding the types of insulation available for the parts of a house and understanding R values.
Introduction: Best House Insulation
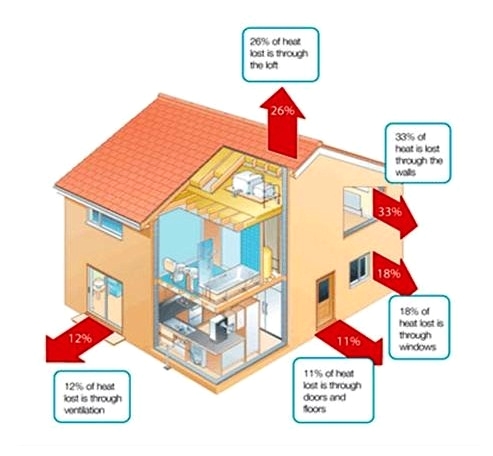
We lose a lot of heat through inadequate insulation in our houses, mainly through the floor, walls, windows, and loft space.
The “R” value of the insulation will give you it’s rating. The R-value is the insulation’s capacity to stop heat from flowing through it, the higher the R-value the better the insulation.
This is an article on house insulation, in particular, examining the best insulation for a house, we begin with R values and then discuss the types of insulation in four main areas of the house.
Must Read:
House Insulation Recommended R Values
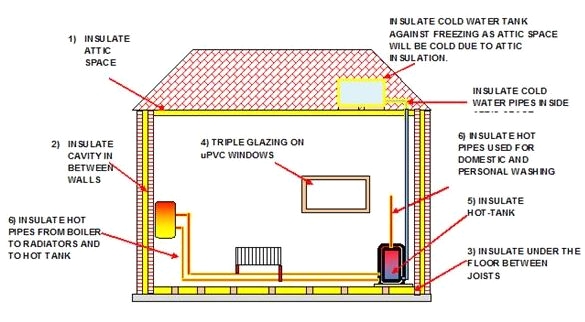
Below is a table indicating the areas of the house that require insulation, against the recommended R values of the insulation type for homes. Areas of the house where insulation is required due to heat loss are also shown in the sketches.
Notes:
- R-value is the resistance of the insulation to resist the transfer of heat through it.
- The R-value units differ between the UK and the USA.
- In the USA different R values are sometimes recommended for the various states; the web link will show which states the R values were taken from.
- UK R values are recorded in m2.K/W (m2.Kelvin/Watt)
- USA R values are recorded in ft²·°F·h/Btu (ft2.°Fahrenheit . hour/British Thermal Unit)
House Insulation Recommended R Values
1. Attic
Flexible Fiberglass Insulation:
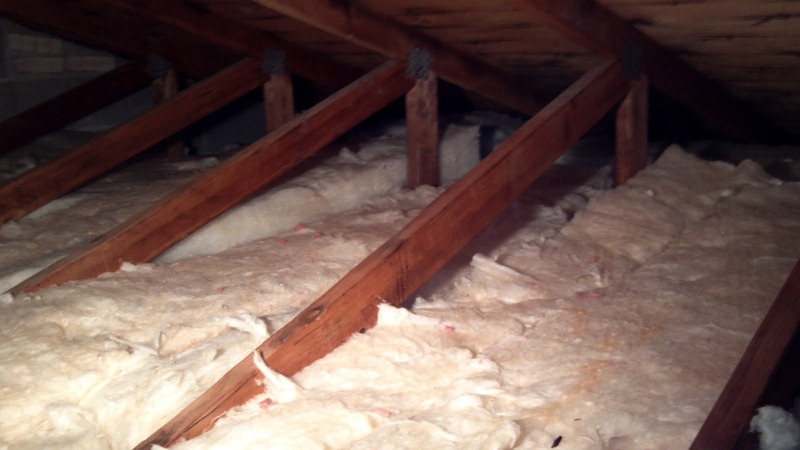

This is supplied in a roll and in widths suitable to be fitted between the joists on the attic floor, the roll is cut to length and available in different thicknesses and R values. Fiberglass is made from recycled ground, spun glass, or rocks. Good quality fiberglass insulation will have an R-value of 3.0/inch thickness.
Loose Fill Insulation:
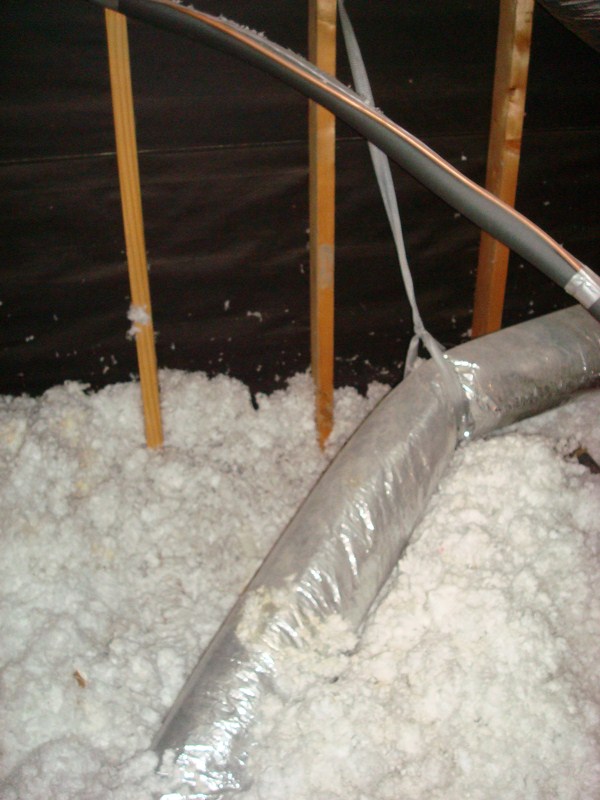

- Cellulose – made from reprocessed paper and card.
- Fiberglass- made from spun glass.
- Rockwool – a similar method of manufacture as fiberglass except for furnace slag (the layer of scum that floats on molten metal) or other similar rock materials are used.
The R-value for loose-fill attic insulation is 3.3/inch thick and is laid between the attic joists.
Cavity Wall Insulation
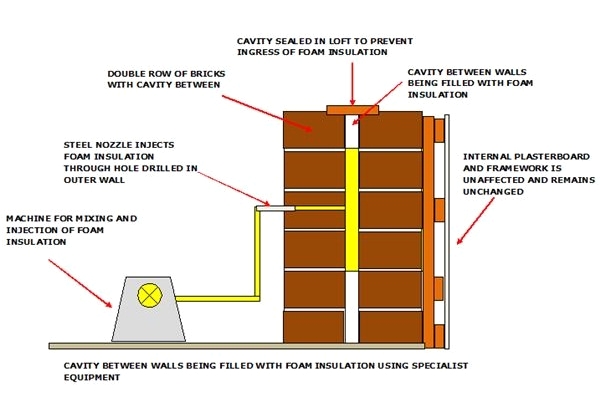
- Polyurethane foam has the highest R-value (6.5/inch thickness) of all the spray-in insulation, but it is also the most expensive.
- Cellulose has an R-value of 3.5/inch thickness. It is manufactured from recycled paper; therefore, it needs to be fireproof.
- Mineral wool insulation has a value of 3.1/inch thickness and is manufactured from furnace slag.
2. External Installation
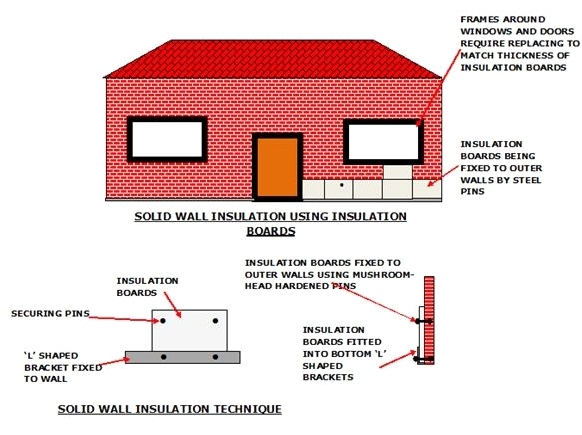

External wall insulation is carried out using insulating boards that are attached to the walls. The R values of the boards are between 4.0/inch thickness and 6.0/inch thickness.
3. Internal Insulation
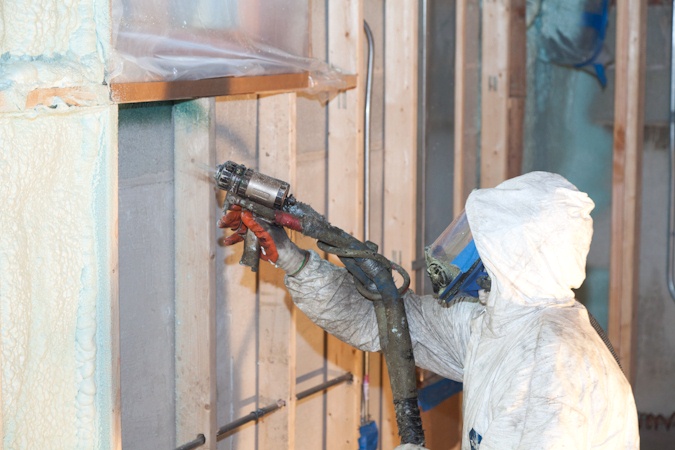

Internal insulation usually involves the removal of plasterboard from the walls. The foam is then applied between the wall studs. Once completed new plasterboard is fitted. Polyurethane has the highest R-value of internal wall insulation being between 4.0 and 6.5/inch thickness.
4. Windows

Window replacement is probably the most expensive of the insulating measures we have examined, and a few types are shown below:

- Frames – these can be of natural wood, or uPVC, which is a synthetic material with good insulating properties.
- Glazing – can be double or triple. The gaps between the sheets of glass can be filled with an inert gas such as argon, which enhances the window’s R-value.
- The glass can also be e-coated with special metal oxide paint that prevents heat loss from the room but permits the passage of heat from the sun into the room.
A good quality double-glazed window will have an R-value of 3.3.
Conclusion
To determine what is the best insulation for a house, it is important to know the R-values and to investigate the various components where loss of heat is suspected.
Safety is important when handling insulation, especially underfloor and loft insulation, as insulation can cause serious skin irritation, eye irritation, and damage to the lungs. Disposable white paper suits, eye protection, gloves, and a breathing mask should, therefore, be worn when working near insulation.










