Japanese cuisine has been quickly growing in popularity over the last few years, and with very good reason, not only is the food very tasty, but it has also been shown to have some incredible health benefits.
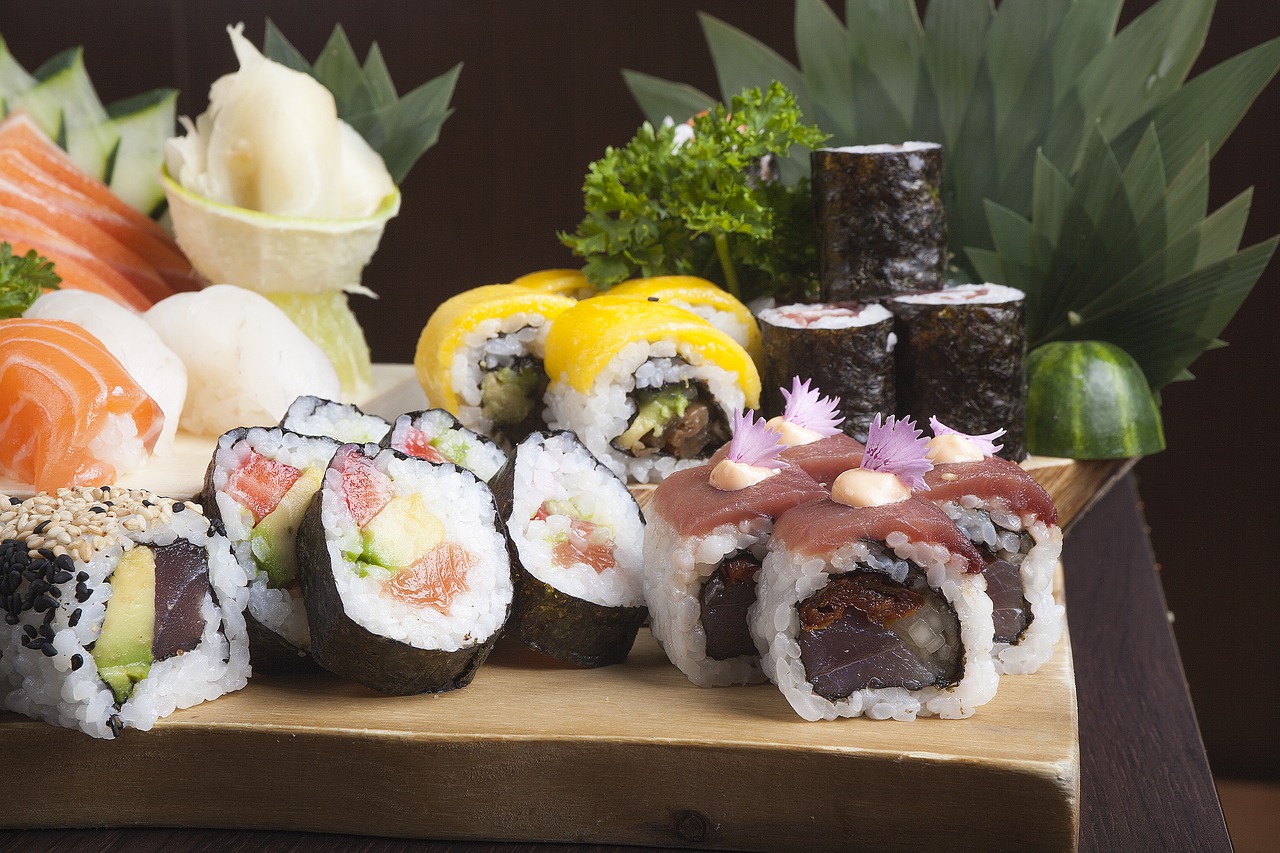

Japanese food can range from the very simple such as ramen to the more complex such as sushi, and it is easy to prepare the food if you have the right tools. The Kitchen Guy has some great comparisons of the things you might need.
A Brief Overview of Japan
Japan is located on the east of the continent of Asia, and consists of almost seven thousand islands, the largest city is Tokyo where a great deal of the population lives.
Japan is located along a long stretch of volcanoes – the most famous of which is Mount Fuji.
This combination of being both islands and having volcanic soil leads to a diet that is rich in a variety of vegetables that can be grown in the fertile land, and a large proportion of fish.
The Japanese Diet
The food that is typically eaten in Japan, as we have said is one that is full of fish and vegetables. A Japanese diet is mainly wholefoods, including rice, noodles, beans, seaweed, and many pickled and fermented foods.
The diet tends to be lower in refined sugars and much lower in fat than other diets. Eggs, dairy, and meat are featured in Japanese food, but these do not form a core part of the food eaten.
Green tea is a very common drink in Japan, with many different varieties such as Jasmine tea and Matcha tea being just a couple of endless varieties.
Many of these food types are eaten raw or cooked, and many are pickled or fermented.
Tofu, which is made from soya beans is eaten in large quantities, as are edamame beans and adzuki beans. Soy is a large part of the diet in Japan, in tofu as mentioned, and it is also fermented to produce natto and miso
Japanese Diet Benefits
Fruit and vegetables in all forms provide a great many vitamins and minerals that are essential for us not just to survive, but to thrive.
A diet rich in fruit and vegetables, high in fibre and low in sugar leads to a longer life span, a better equipped immune system, and less old age-related illnesses.
Fermented foods, such as miso, or in other countries, sauerkraut, are well documented for having a positive influence on the digestive system and the immune system, which is thought to be linked to the excellent probiotic properties of fermented foodstuffs.
Fish is eaten commonly, often in the form of sushi and sashimi, fish is well known for its brain-boosting properties with its high omega three and six content.
Vitamin D is also found in oily fish like salmon, vitamin D is often lacking in modern-day diets, which can cause many problems, including a lack of energy.
Seaweed is consumed more in Japan than almost anywhere else. Seaweed has many health benefits, but is most notably known for its B12 content, a vitamin that most people don’t get enough of, and is vital for many functions within the body
Green tea has been heavily researched in recent years and has become very popular for its antioxidant properties, which are linked to having a stronger immune system, and there seems to be some evidence that green tea can help lower the risk of heart disease and some cancers.
Eating Smaller Portions
The Japanese are seen as having a very healthy attitude towards food, and culturally people are taught to eat until only 80% full, and this helps people to not overeat, and enjoy the food they are eating.
In Western countries, food is usually served on a large dinner plate, that is often piled with food, and it is considered rude to leave any food on your plate.
Japan differs from this by serving several different foods on small plates, and the diner will place some in a small bowl that they use to eat from, and food is normally eaten with chopsticks.
Food is often a social event, either at home around a table, or in restaurants, and so food is seen as a pleasure to be enjoyed.
Snacking is a treat to be enjoyed occasionally, not as a routine part of the day, and snacks are kept small.
Increased Life Span
Japanese people have some of the longest life expectancies in the world, in fact, the island of Okinawa has been labelled a Blue Zone, which means that residents have an exceptionally high life span, often living past one hundred years old.
The diet on Okinawa is similar to that of the typical Japanese diet but has a large amount of sweet potatoes included.
A traditional Japanese diet may safeguard against chronic illnesses such as heart disease and type 2 diabetes. Salt can be increased in the diet due to components like soy sauce, but sodium-reduced ingredients can be easily sourced.
Despite this slightly increased salt content, heart disease is less prevalent here than elsewhere in the world.
Variety of Foods
There are so many different types of food available in Japan, and this leads to the cuisine being not only very healthy, but also delicious, and never boring. There are never-ending combinations that can be made.
Of course, as with everywhere in the world as we become more connected via transport and the internet, it is now very easy to find processed and unhealthy food in Japan, and anyone who eats a diet high in processed foods, full of refined sugars and trans-fats will not see a benefit to their health.
A traditional Japanese diet, high in whole foods and low in sugar and fat, with good portion control, has lots of evidence to prove that it is good for your general health, good at keeping your weight at a healthy level and could increase your lifespan.